The world is changing towards
energy transition
Fossil fuel investment is declining and will be largely offset by a 150% increase in renewable energy supply investment between 2015 and 2050. To meet the Paris Climate Agreement’s goals, total demand side investment into low carbon technologies and services would need to grow by a factor of 10 over the same period, reaching nearly $3 trillion annually in the 2040s.
The transformation to new energy
The traditional power grid of centralized one-way power system will be replaced with two-way distributed power system through energy evolution.
The transformation from a centralized power system to a distributed power system involves a shift in the way electricity is generated, distributed, and consumed. In a centralized power system, electricity is primarily generated at
large power plants located at centralized locations. This electricity is then transmitted over long distances through a network of transmission lines to reach consumers.
On the other hand, in a distributed power system, electricity generation is decentralized, with power being generated at various small-scale sources located closer to the point of consumption. These sources can include rooftop solar
system, wind turbines, microgrids, and energy storage systems. The electricity generated from these distributed sources is used locally, reducing the need for extensive transmission and distribution infrastructure.
The transformation from a centralized power system to a distributed power system represents a fundamental shift towards a more resilient, sustainable, and consumer-centric energy infrastructure. It brings about benefits in terms
of reliability, renewable energy adoption, and consumer empowerment, contributing to a more efficient and greener energy future.
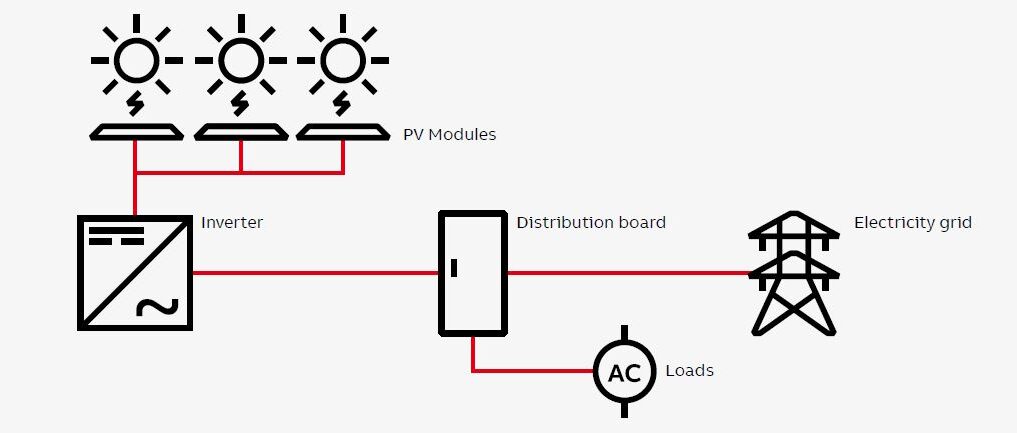
Grid-Connected System
A grid-connected solar system is a renewable energy solution that enables solar panels to generate electricity directly connected to the electrical grid. The system comprises solar panels, a grid-tied inverter and a bi-directional meter. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity, which is then converted to AC electricity through the inverter for use in homes or businesses.
Any excess electricity produced is fed back into the grid through the bi-directional meter, earning credits to reduce future electricity bills through net metering. Grid-connected solar systems offer benefits such as reduced reliance on fossil fuels, cost savings through net metering, and a stable power supply by seamlessly drawing electricity from the grid when needed.
Off-Grid System
An off-grid solar system, also known as a standalone solar system, is a self-contained renewable energy solution that operates independently of the electrical grid. It is designed to provide electricity in remote areas or locations where access to the utility grid is limited or non-existent.
The energy generated in an off-grid solar system will be stored in batteries. The stored energy will be drawn to power the electrical loads when the sun is not available during nighttime or raining days.
Off-grid solar system offer energy independence and reliability in areas where grid access is limited or unreliable. It provide a sustainable and clean alternative to traditional diesel fuel generators, reducing dependence on non-renewable energy sources and minimizing carbon emissions. These systems are particularly beneficial for remote areas, off-grid communities and outdoor applications where access to the utility grid is impossible.
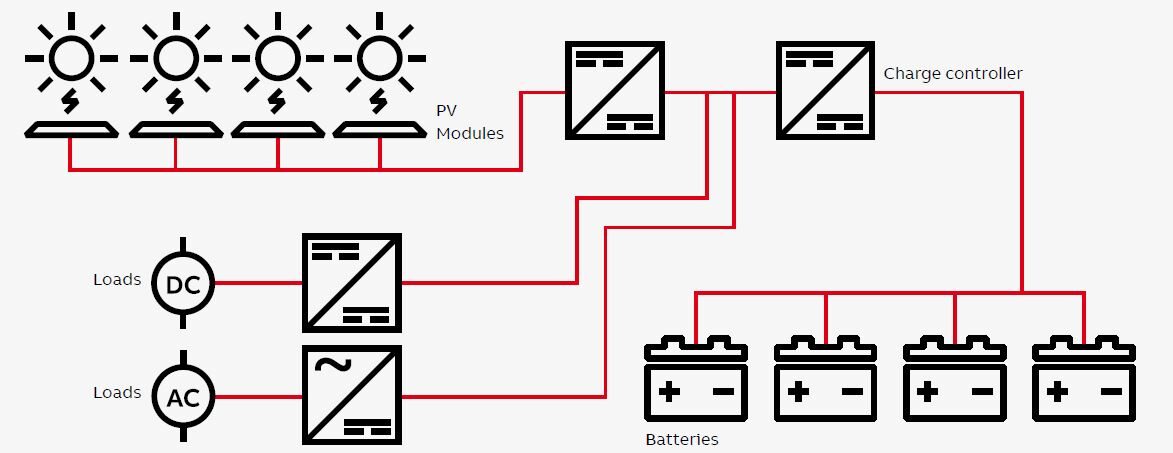
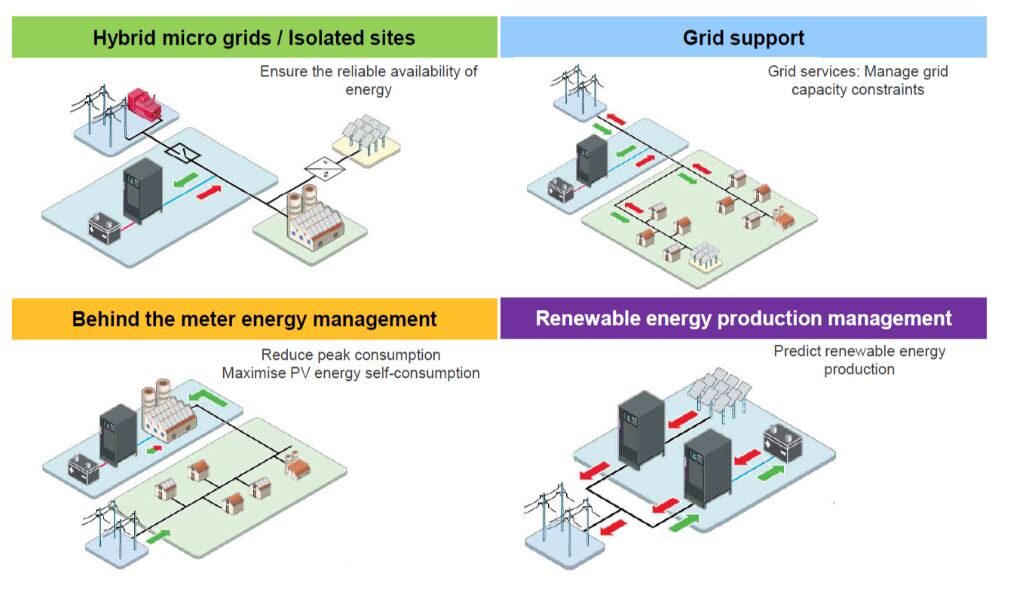
Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)
A battery energy storage system (BESS) is a technology that stores electrical energy in batteries for later use. It plays a crucial role in the integration of renewable energy sources and helps to overcome the intermittency and variability of renewable power generation, such as solar and wind.
In a battery energy storage system, electricity is stored in rechargeable batteries when it is abundantly available, such as during periods of low energy demand or high renewable energy generation. The stored energy can then be discharged when needed, such as during peak demand periods or when renewable energy generation is low. This enables a more balanced and reliable supply of electricity.
BESS offers several benefits. It provides a solution for managing fluctuations in renewable energy generation, ensuring a smooth and stable power supply. It also enables energy arbitrage, allowing users to buy electricity from the grid when prices are low and store it for use when prices are high. Additionally, battery storage systems can provide backup power during outages or serve as an alternative to diesel generators in remote areas.
The use of battery energy storage systems is growing rapidly as the costs of batteries decline and their performance improves. They are being deployed at various scales, from residential and commercial applications to utility-scale projects, contributing to the development of more resilient and sustainable energy systems.
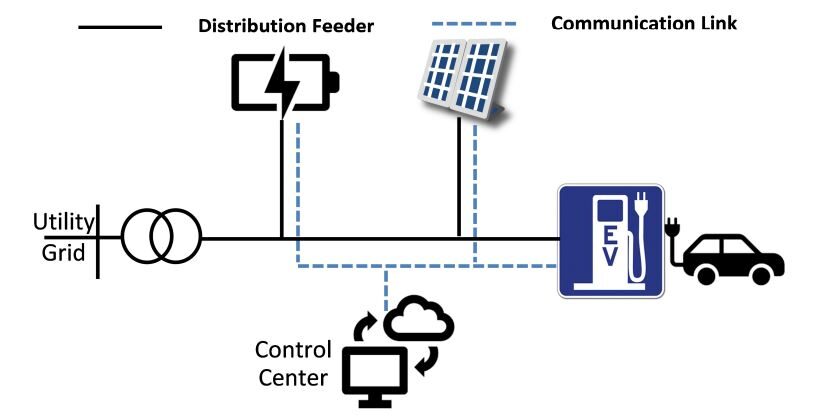
EV Charging System
An electric vehicle (EV) charging system is a critical component of the infrastructure needed to support the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. It is designed to supply electricity to recharge the batteries of electric vehicles, allowing them to travel longer distances and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
EV charging systems come in various forms, ranging from residential charging stations to public charging stations located in parking lots, streets, and highways. They provide a safe and convenient way for EV owners to recharge their vehicles at home or on the go.
These charging systems typically include a charging unit, known as an EV charger, and connectors that allow the EV to be plugged into the charging infrastructure. The charging unit manages the flow of electricity to the vehicle’s battery, ensuring efficient and safe charging.
As the popularity of electric vehicles continues to grow, the development of robust and widespread EV charging systems is crucial for the successful transition to a sustainable transportation future. Governments, businesses, and individuals are investing in the deployment of charging infrastructure to support the increasing number of electric vehicles on the road and accelerate the shift towards cleaner and greener transportation.